# 整体流程
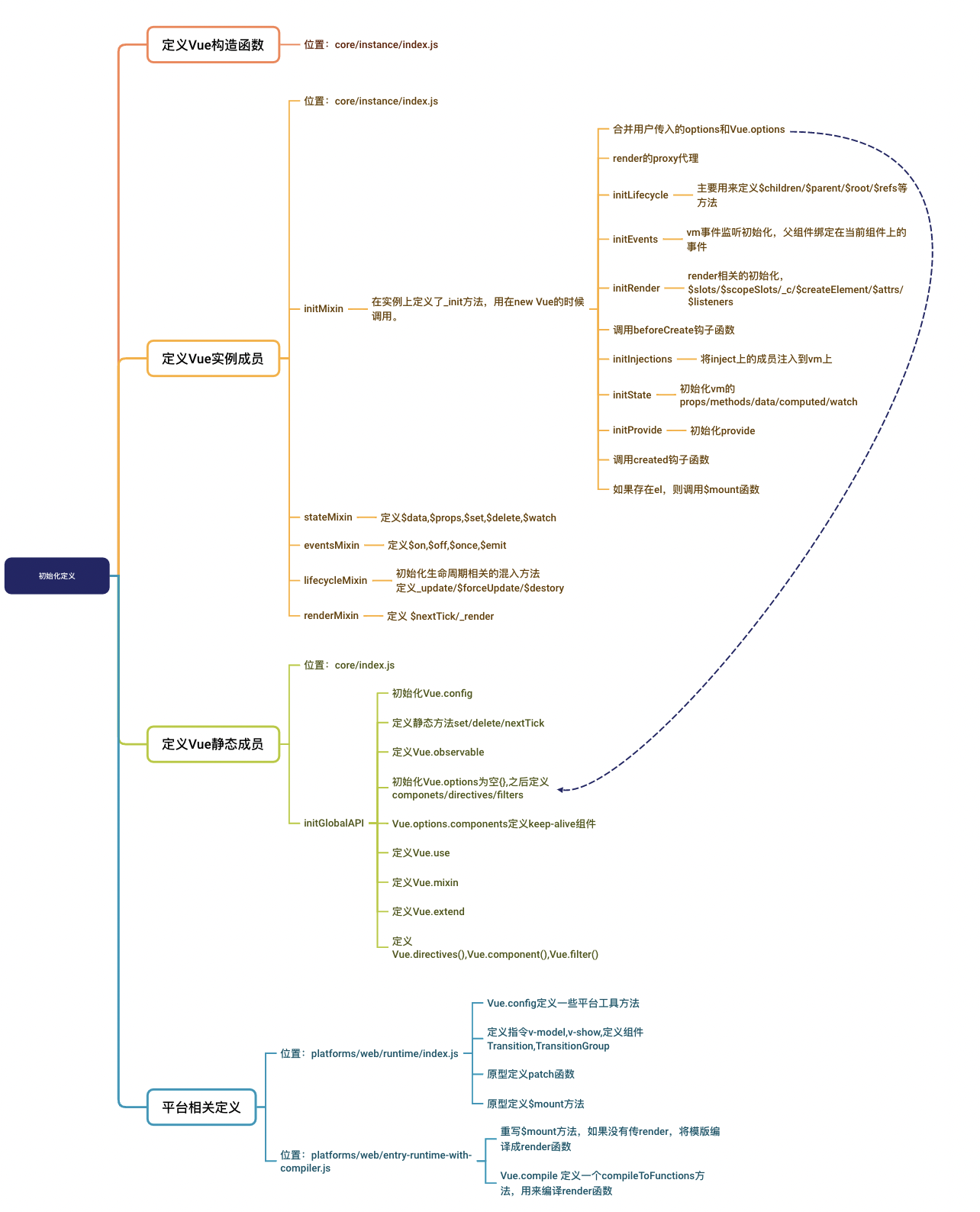
# 初始化定义
在之前的总结中我们知道Vue会根据不同的环境(Web,Weex)找到不同的入口文件,最终都会去import Vue的构造函数,我们需要理解Vue构造函数执行的整个流程。
我们以entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 作为分析的入口,逐层寻找,最后通过分析,我们可以得到一份简单的定义流程图
# initMixin
从之前的分析中,我们得知initMixin主要用来定义_init方法
function Vue(options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && !(this instanceof Vue)) {
warn("Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword");
}
// 执行_init,同时传入用户的options
this._init(options);
}
当我们使用的时候,则会执行_init
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: "hello world",
},
});
然后我们看下_init是如何定义的
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
const vm: Component = this;
// 合并用户传入的options和Vue构造函数中设置的options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
initInternalComponent(vm, options);
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm,
);
}
// render代理
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
initProxy(vm);
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm;
}
vm._self = vm;
// vm生命周期相关变量初始化
// $children/$parent/$root/$refs
initLifecycle(vm);
// vm事件监听初始化,父组件绑定在当前组件上的事件
initEvents(vm);
// vm的render初始化
// $slots/$scopeSlots/_c/$createElement/$attrs/$listeners
initRender(vm);
// 钩子函数执行
callHook(vm, "beforeCreate");
// 将inject上的成员注入到vm上
initInjections(vm);
// 初始化vm的props/methods/data/computed/watch
initState(vm);
// 初始化provide
initProvide(vm);
// 钩子函数执行
callHook(vm, "created");
// 调用$mount挂载
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el);
}
};
};
状态相关的,$mount等我们在具体执行的时候再去分析。
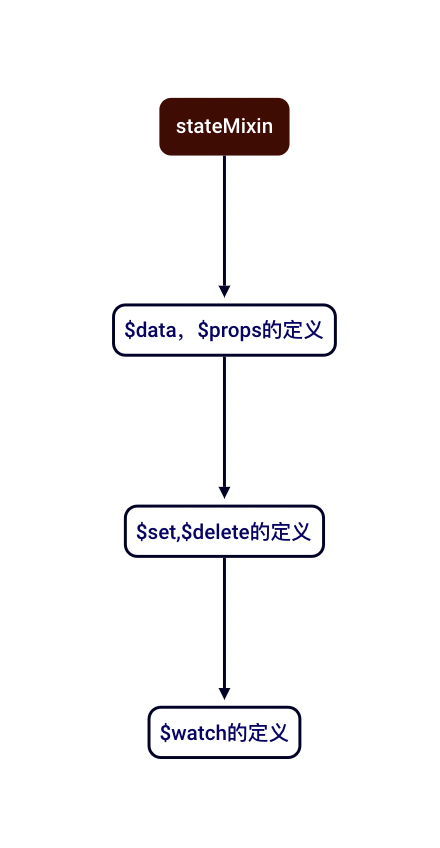
# stateMixin
stateMixin主要用来定义Vue实例上的属性和方法,包括$data,$props,$set,$delete,$watch
import { set, del } from "../observer/index";
export function stateMixin(Vue) {
// 定义$data, $props
const dataDef = {};
dataDef.get = function () {
return this._data;
};
const propsDef = {};
propsDef.get = function () {
return this._props;
};
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, "$data", dataDef);
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, "$props", propsDef);
// 定义$set, $delete, $watch
Vue.prototype.$set = set;
Vue.prototype.$delete = del;
Vue.prototype.$watch = function () {};
}
$data和$props: 通过代理的方式获取到_data和_props,同时不能set改变对应的数据,在开发模式会抛出warning。
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
dataDef.set = function () {
warn(
"Avoid replacing instance root $data. " +
"Use nested data properties instead.",
this
);
};
propsDef.set = function () {
warn(`$props is readonly.`, this);
};
}
`$set`和`delete`: 和全局的`Vue.set`,`Vue.delete`为同一个方法,主要是处理响应式数据,我们后面会详细分析。
`$watch`: 通过一个`watcher`实例来监听,后续会详细介绍。
流程图:
# eventsMixin
eventsMixin主要用来定义事件相关的实例方法:$on,$once,$off,$emit。
仔细看源码其实就是发布-订阅模式来处理一些事件
# 定义$on
const hookRE = /^hook:/;
Vue.prototype.$on = function (event, fn) {
const vm = this;
if (Array.isArray(event)) {
for (let i = 0, l = event.length; i < l; i++) {
vm.$on(event[i], fn);
}
} else {
(vm._events[event] || (vm._events[event] = [])).push(fn);
if (hookRE.test(event)) {
vm._hasHookEvent = true;
}
}
return vm;
};
在initMixin中会初始化事件相关的initEvents,定义了初始化的_events对象
export function initEvents(vm: Component) {
// 存储事件名称和对应的处理函数
vm._events = Object.create(null);
vm._hasHookEvent = false;
// init parent attached events
// 获取父元素上附加的事件
const listeners = vm.$options._parentListeners;
// 注册自定义事件
if (listeners) {
updateComponentListeners(vm, listeners);
}
}
分析:首先判断事件是否为数组,如果不是,则定义为fn到_events中,否则则会遍历数组,递归的去调用$on方法。
# 定义$emit
Vue.prototype.$emit = function (event) {
const vm = this;
let cbs = vm._events[event];
if (cbs) {
cbs = cbs.length > 1 ? toArray(cbs) : cbs;
const args = toArray(arguments, 1);
const info = `event handler for "${event}"`;
for (let i = 0, l = cbs.length; i < l; i++) {
invokeWithErrorHandling(cbs[i], vm, args, vm, info);
}
}
return vm;
};
分析:我们从_events中获取到对应的方法,然后遍历进行调用。这边用了invokeWithErrorHandling来包裹,更好的处理错误。
# 定义$off
Vue.prototype.$off = function (event, fn) {
const vm = this;
// all
if (!arguments.length) {
vm._events = Object.create(null);
return vm;
}
// array of events
if (Array.isArray(event)) {
for (let i = 0, l = event.length; i < l; i++) {
vm.$off(event[i], fn);
}
return vm;
}
// specific event
const cbs = vm._events[event];
if (!cbs) {
return vm;
}
if (!fn) {
vm._events[event] = null;
return vm;
}
// specific handler
let cb;
let i = cbs.length;
while (i--) {
cb = cbs[i];
if (cb === fn || cb.fn === fn) {
cbs.splice(i, 1);
break;
}
}
return vm;
};
分析:主要是事件的取消订阅,首先如果不传参数,则取消所有的事件监听,如果只传了event,则取消该event下面的所有事件监听,如果传了event和fn,则取消对应fn下面的事件监听。
# 定义$once
Vue.prototype.$once = function (event, fn) {
const vm = this;
function on() {
vm.$off(event, on);
fn.apply(vm, arguments);
}
on.fn = fn;
vm.$on(event, on);
return vm;
};
分析:将fn定义在内部的on函数上,可以在后续的移除操作中使用这个回调函数。执行完on函数后直接off可以确保fn只执行一次,可以学习一下这种设计模式,有效保证了函数的私有性和封装性。
//cb.fn是once定义
if (cb === fn || cb.fn === fn) {
cbs.splice(i, 1);
break;
}
# lifecycleMixin
lifecycleMixin主要用来定义生命周期相关的方法,包括_update,$forceUpdate,$destory
export function lifecycleMixin(Vue) {
Vue.prototype._update = function () {};
// 实例方法
Vue.prototype.$forceUpdate = function () {
if (this._watcher) {
this._watcher.update();
}
};
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {};
}
生命周期的相关功能会在后面详细展开
# renderMixin
renderMixin 主要用来定义一堆私有方法,还有nextTick,_render
export function renderMixin(Vue) {
// 挂载各种私有方法,例如this._c,this._v等
installRenderHelpers(Vue.prototype);
Vue.prototype.$nextTick = function (fn) {
return nextTick(fn, this);
};
Vue.prototype._render = function () {};
}
installRenderHelpers :定义私有方法
export function installRenderHelpers(target: any) {
target._o = markOnce;
target._n = toNumber;
target._s = toString;
target._l = renderList;
target._t = renderSlot;
target._q = looseEqual;
target._i = looseIndexOf;
target._m = renderStatic;
target._f = resolveFilter;
target._k = checkKeyCodes;
target._b = bindObjectProps;
target._v = createTextVNode;
target._e = createEmptyVNode;
target._u = resolveScopedSlots;
target._g = bindObjectListeners;
target._d = bindDynamicKeys;
target._p = prependModifier;
}
nextTick: 和全局的nextTick()为同一个方法。
_render():编译模版为VNode。
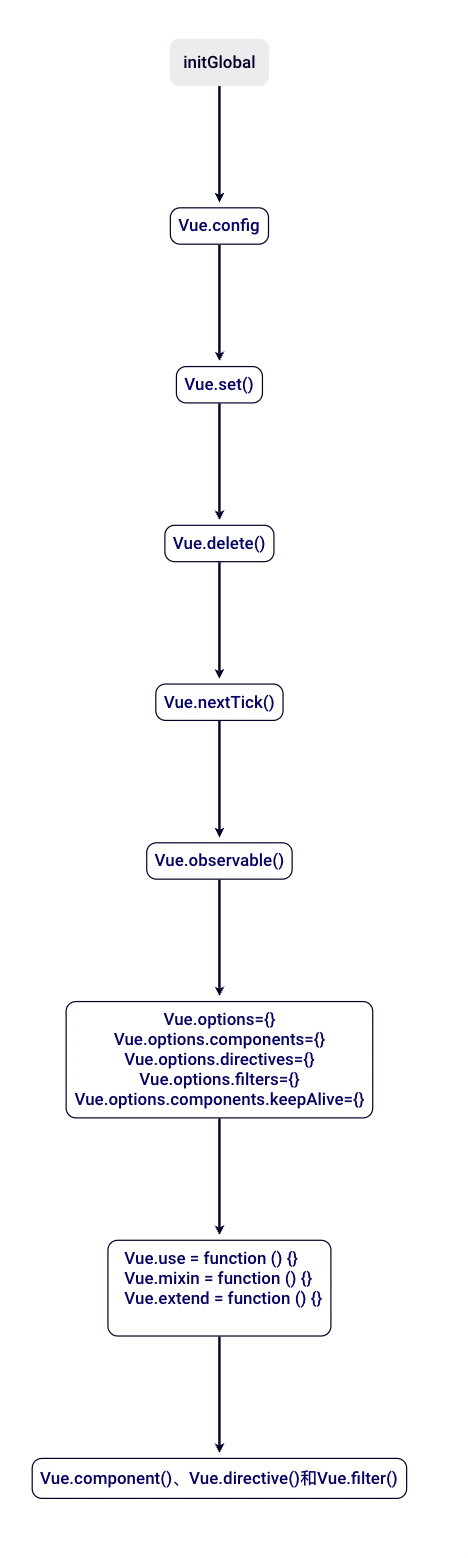
# initGlobalAPI
定义完实例相关的方法后,initGlobalAPI主要用来挂载全局的方法。
export function initGlobalAPI(Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// config
const configDef = {};
configDef.get = () => config;
// 初始Vue.config
Object.defineProperty(Vue, "config", configDef);
Vue.util = {
warn,
extend,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive,
};
// 定义静态方法set/delete/nextTick
Vue.set = set;
Vue.delete = del;
Vue.nextTick = nextTick;
// 2.6 explicit observable API
Vue.observable = (obj) => {
observe(obj);
return obj;
};
// 初始化Vue.options, 设置原型为null的对象,提高性能
Vue.options = Object.create(null);
// 给Vue.options定义 componets/directives/filters为空对象
ASSET_TYPES.forEach((type) => {
Vue.options[type + "s"] = Object.create(null);
});
// this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain-object
// components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios.
Vue.options._base = Vue;
// 设置keep-alive组件
extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents);
// 注册Vue.use()来注册插件
initUse(Vue);
// 注册Vue.mixin()来实现混入
initMixin(Vue);
// 注册Vue.extend()基于传入的options返回一个组件的构造函数
initExtend(Vue);
// 注册Vue.directives(),Vue.component(),Vue.filter()
initAssetRegisters(Vue);
}
整体的逻辑其实很清晰:
我们分析的是Web平台的代码,所以还要看入口runtime+compile的逻辑
platforms/web/runtime/index.js:
主要是定义了一些工具方法,同时扩展了directives和components,加入了v-model,v-show,Transition组件,TransitionGroup组件,还在原型中定义了 __patch__方法用来更新虚拟DOM,定义了$mount用来挂载Dom。
Vue.config.mustUseProp = mustUseProp;
Vue.config.isReservedTag = isReservedTag;
Vue.config.isReservedAttr = isReservedAttr;
Vue.config.getTagNamespace = getTagNamespace;
Vue.config.isUnknownElement = isUnknownElement;
extend(Vue.options.directives, platformDirectives);
extend(Vue.options.components, platformComponents);
Vue.prototype.__patch__ = inBrowser ? patch : noop;
Vue.prototype.$mount = function () {};
platfomrs/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
主要是重写了$mount,用来渲染template转成render函数,同时定义了 Vue.compile 函数用来编译成Vnode
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount;
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el, hydrating) {
// ...
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(
template,
{
outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production",
shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments,
},
this
);
options.render = render;
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns;
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating);
};
// 定义compile
Vue.compile = compileToFunctions;
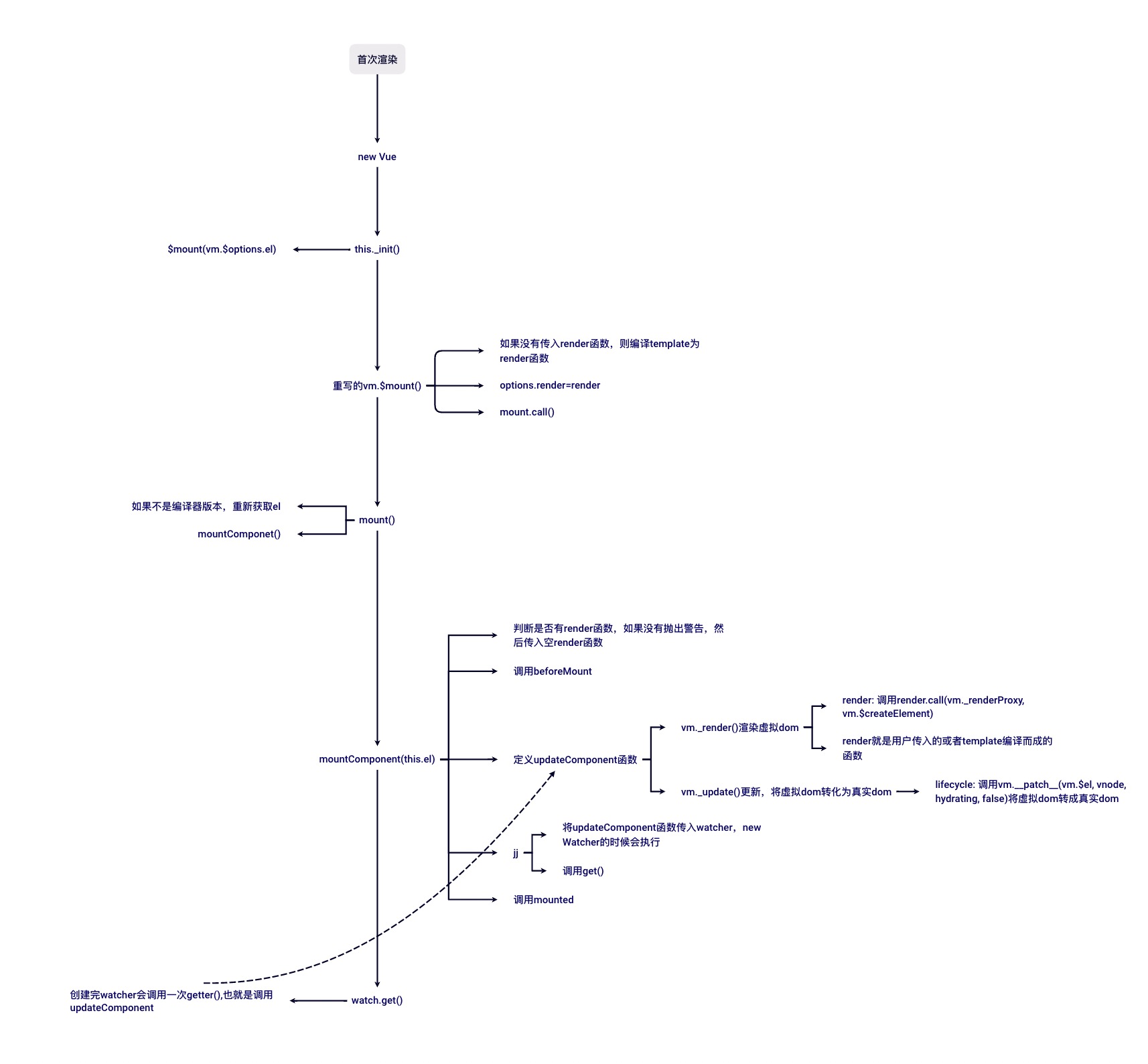
# 首次渲染
上面分析的所有都是Vue相关的定义,当我们new Vue的时候,才是代码执行,进行首次渲染的逻辑,按照分析,我们得出一个流程图