# 派发更新
# Watcher
Vue.js 源码中 Watcher 分为 3 种:render Watcher,computed Watcher,user Watcher。派发更新就是当响应式数据变化的时候去触发渲染视图,计算属性,执行user函数。
一共有 4 处派发更新的地方:
- 七种数组变异方法。
const methodsToPatch = [
"push",
"pop",
"shift",
"unshift",
"splice",
"sort",
"reverse",
];
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) {
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator(...args) {
ob.dep.notify();
return result;
});
});
- Vue.set 或者 this.$set
export function set(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any, val: any): any {
defineReactive(ob.value, key, val);
ob.dep.notify();
return val;
}
- Vue.delete 或者 this.$delete
export function del(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any) {
delete target[key];
if (!ob) {
return;
}
ob.dep.notify();
}
- defineReactive 的 Object.defineProperty()中的 setter
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {},
set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
// ...
dep.notify();
},
});
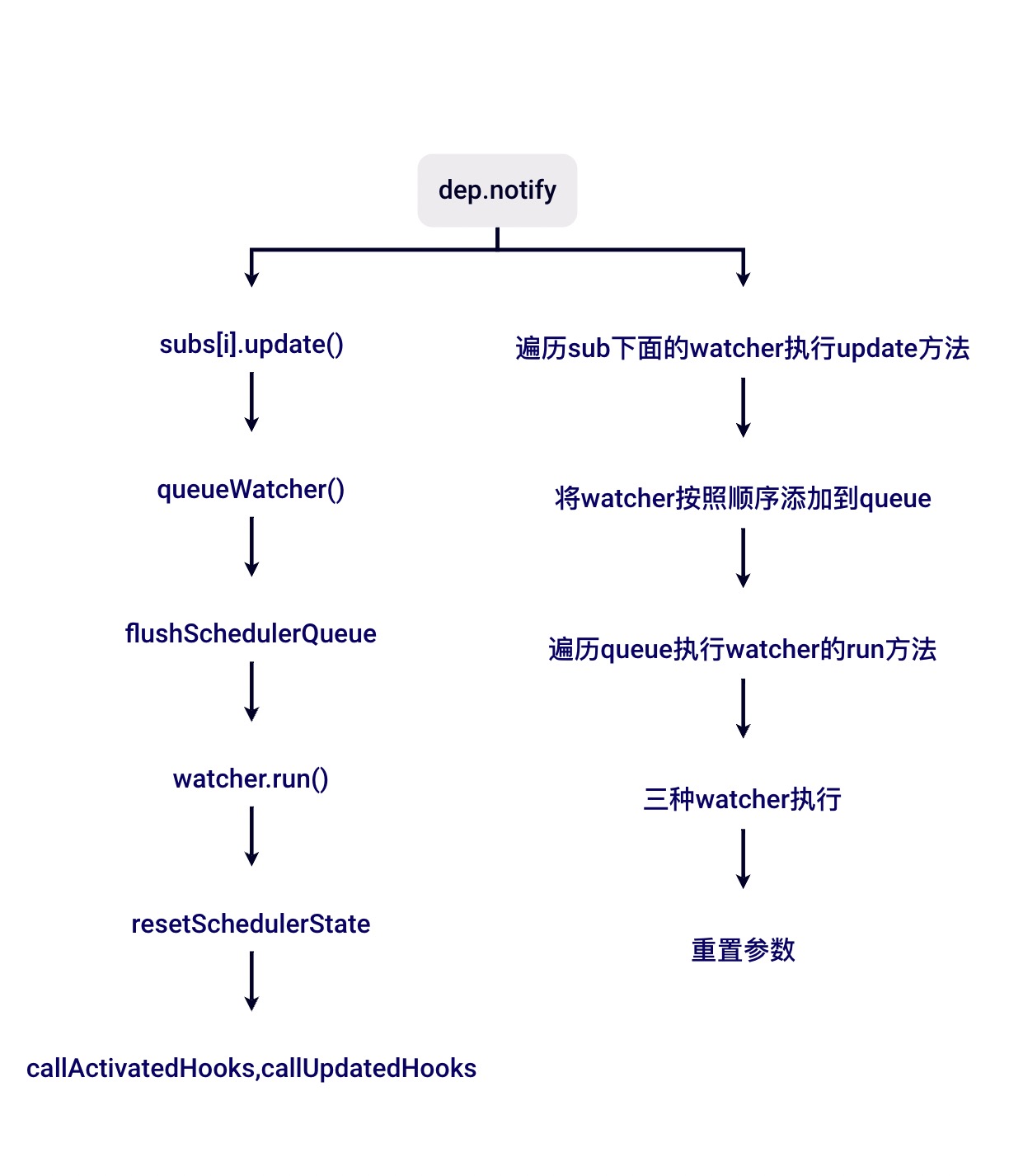
# dep.notify()
dep.notify()就是关键的执行派发更新的代码。
class Dep {
notify() {
const subs = this.subs.slice();
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && !config.async) {
subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id);
}
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update();
}
}
}
逻辑也很简单,我们知道 subs 存的是 Watcher,主要就是遍历 subs 数组,然后调用 Watcher的update 方法。
import { queueWatcher } from "./scheduler";
class Watcher {
update() {
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true;
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run();
} else {
queueWatcher(this);
}
}
}
this.lazy为true表示是一个computed Watcher,render watcher 主要看的是queueWatcher。
const queue: Array<Watcher> = [];
let has: { [key: number]: ?true } = {};
let waiting = false;
let flushing = false;
let index = 0;
export function queueWatcher(watcher: Watcher) {
const id = watcher.id;
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true;
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher);
} else {
let i = queue.length - 1;
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--;
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher);
}
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true;
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && !config.async) {
flushSchedulerQueue();
return;
}
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue);
}
}
}
- queue: 所有的 Watcher 都会注入到
queue队列。 - has : 一个对象,用来防止重复
Watcher。 - flushing: 如果为真,说明当前
queue队列正在被处理。
整个流程就是判断下 watcher id是否存在,如果不存在,判断是否在 flushing 状态和 waiting 状态,最后在下一个 tick 执行 flushSchedulerQueue。
function flushSchedulerQueue() {
currentFlushTimestamp = getNow();
flushing = true;
let watcher, id;
// 1.组件update从父->子,2.用户watcher在渲染watcher之前执行(initState早于mountComponent)3.如果一个组件在父组件执行之前被销毁,则跳过
queue.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id);
for (index = 0; index < queue.length; index++) {
watcher = queue[index];
if (watcher.before) {
watcher.before();
}
id = watcher.id;
has[id] = null;
watcher.run();
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && has[id] != null) {
circular[id] = (circular[id] || 0) + 1;
if (circular[id] > MAX_UPDATE_COUNT) {
warn(
"You may have an infinite update loop " +
(watcher.user
? `in watcher with expression "${watcher.expression}"`
: `in a component render function.`),
watcher.vm
);
break;
}
}
}
const activatedQueue = activatedChildren.slice();
const updatedQueue = queue.slice();
resetSchedulerState();
callActivatedHooks(activatedQueue);
callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue);
}
首先是设置flushing为true,防止在执行的时候,有Watcher进queue,之后对queue内的watcher进行排序,这是为了保证:
- 1.组件 update 从父->子,保证先处理父级的 render watcher .
- 2.user watcher 在 render watcher 之前执行(initState 是在 mountComponent 之前执行).
- 3.如果一个组件在父组件执行之前被销毁,则子组件所有的 watcher 跳过
接着遍历queue,queue的长度可能变化,所以不缓存length,然后会释放掉has,因为数据变化的时候,watcher可能会再次进来执行,然后执行watcher的run方法。
class Watcher {
run() {
if (this.active) {
const value = this.get();
if (value !== this.value || isObject(value) || this.deep) {
const oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
if (this.user) {
const info = `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`;
invokeWithErrorHandling(
this.cb,
this.vm,
[value, oldValue],
this.vm,
info
);
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue);
}
}
}
}
}
render watcher: 直接执行this.get(),内部会执行this.getter(),也就是vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)user watcher: 就会执行invokeWithErrorHandling,其实就是执行this.cb.call(),只是做了一层错误处理computed watcher: 则会执行this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
最后resetSchedulerState还原状态,触发activated,updated钩子函数。
需要考虑一种特殊的情况:
export default {
watch: {
a() {
this.a = Math.random();
},
},
};
当我们执行完 user watcher 后,由于改变了 this.a,所有会再次触发 setter,这个时候又再次调用了 watcher.run(),这个时候会触发死循环,所以有了一个最大次数的限制。
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && has[id] != null) {
circular[id] = (circular[id] || 0) + 1;
if (circular[id] > MAX_UPDATE_COUNT) {
warn(
"You may have an infinite update loop " +
(watcher.user
? `in watcher with expression "${watcher.expression}"`
: `in a component render function.`),
watcher.vm
);
}
}
# 流程图